PURPOSE To evaluate magnetic resonance (MR) imaging findings of the spine in patients with GuillainBarré syndrome MATERIALS AND METHODS MR imaging findings in eight patients (three male, five female; GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is an idiopathic, immunemediated attack of the peripheral nervous system, with patients most commonly presenting with bilateral, ascending weakness, and loss of deep tendon reflexes Considered an extremely rare postoperative complication, particularly in cervical spine patients, we report a unique case of GBSThe Guillain–Barré syndrome is an immunologically mediated condition affecting the peripheral nervous system There is evidence that Guillain–Barré syndrome, Miller–Fisher syndrome, and Bickerstaff brain stem encephalitis form a closely related spectrum of disorders1 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) abnormalities in the spinal cord in these conditions have been well

Pdf Spinal Mri Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome
Guillain barre syndrome mri cervical spine
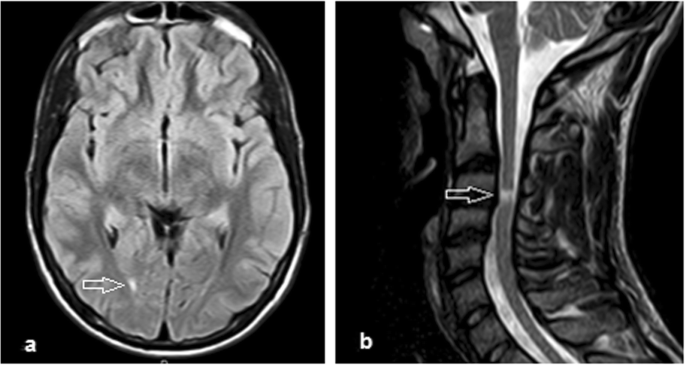
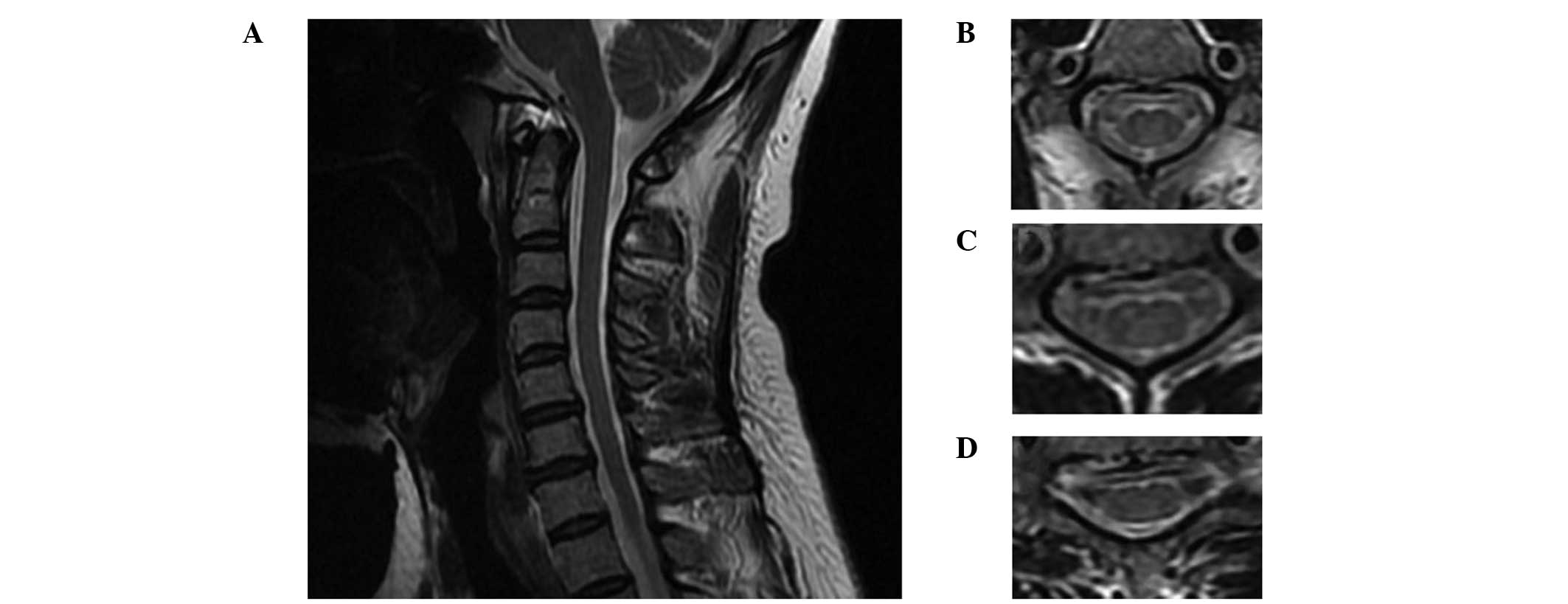
Guillain barre syndrome mri cervical spine-Figure 1 Cerebral cervical spine MRI of a 43yearold female with GuillainBarre syndrome presenting with acute bilateral vision deficit (AF) Brain MRI indicated bilateral hemispheric symmetry and no focal abnormalities of signal The ventricles of the brain, midline structures, subtentorial cerebellar and brainstem appeared normal We very much enjoyed reading the article by OguzAkarsu and colleagues describing GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) in a coronavirus disease19 (COVID19) patient with minimal systemic manifestations 1 The patient was admitted with a 3day history suggestive of GBS We focused on the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study of the lumbar and cervical spines




Mri Of The Spinal Cord In A 3 Year Old Boy With Guillain Barre Download Scientific Diagram
GuillainBarré syndrome is a relatively common, acute, and rapidly progressive, inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy The diagnosis is usually established on the basis of symptoms and signs, aided by cerebrospinal fluid findings and electrophysiologic criteriaCoincidence of GuillainBarre Syndrome in a Patient with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy, A Case Report Talal M AlHarbi1*, Sameeh O Abdulmana 1, Mohammed Bin Falah2 and Reem F Bunyan1 1Department of Neurology, Neurosciences Centre, King Fahad Specialist Hospital, 60 Ammar Bin Thabet St, Al Muraikabat, Dammam , Saudi Arabia 2University Medical These tests can help doctors exclude other possible causes of severe weakness, which may resemble GuillainBarré syndrome For example, MRI can help exclude spinal cord damage due to compression Compression of the Spinal Cord Injuries and disorders can put pressure on the spinal cord, causing back or neck pain, tingling, muscle weakness, and
Full spine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a brainstem and cervical leptomeningeal enhancement Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) revealed albumincytological dissociation Microbiological studies on CSF, including SARSCoV2, were negative Nerve conduction studies were consistent with demyelinating neuropathy COVID19 has become a pandemic It affects multiple systems of the body including the nervous system It invades the nervous systems through multiple routes either olfactory tract, bloodstream (by binding to endothelial receptors) or via ACE2 receptors in the brain We report a case of GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) variant (acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN type)) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has become the examination of choice for imaging the spine and its contents Normal cervical spine (A) Axial T2weighted image demonstrates a small high signal plaque within the right dorsolateral cervical cord Guillain–Barré syndrome (acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy) is
CASE REPORTS / CASE SERIES 441 GuillainBarré syndrome following thoracic spinal cord trauma Syndrome de GuillainBarré à la suite d'un traumatisme de la moelle épinière thoracique James Scozzafava MD,*Glen Jicking MD,† Jack H Jhamandas MD PhD,† Michael J Jacka MD MSc‡ Purpose GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is an acute immuno CAN J ANESTH 08 / 55 7 / pp INTRODUCTION Neck and arm pains with weakness are a common complaint that typically represents a spectrum of cervical spine disorders In such patients with arm and neck pains with weakness, physicians must pay attention to the clinical history and examination of patients including diagnostic studies such as plain radiography, magnetic resonance image (MRI GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks part of its peripheral nervous system—the network of nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord GBS can range from a very mild case with brief weakness to nearly devastating paralysis, leaving the person unable to




Pdf Spinal Mri Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome




Cervical Spine Surgery Complicated By Postoperative Guillain Barre Syndrome Sciencedirect
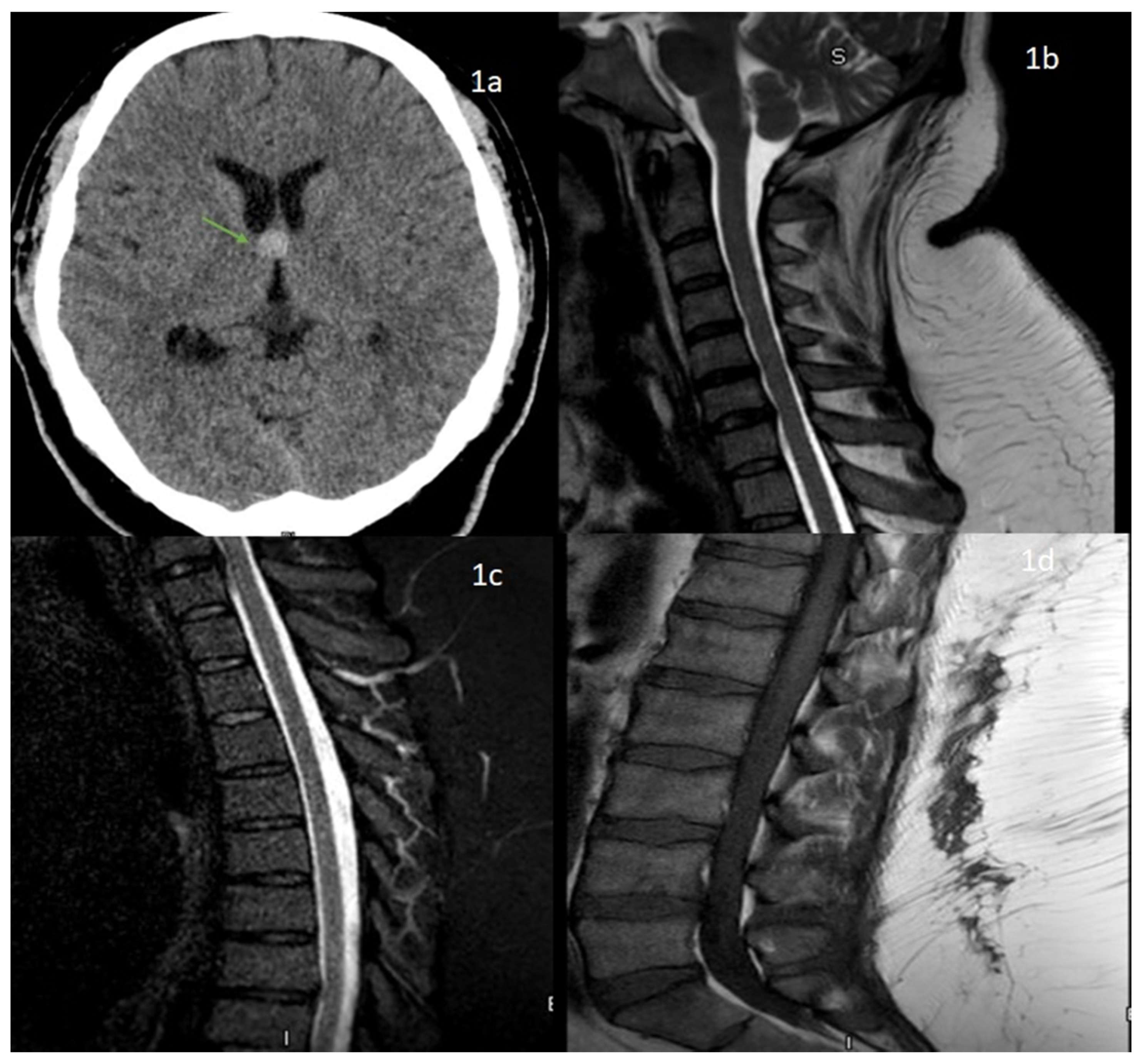
MRI brain with the cervical spine and brachial plexus performed at a local center had been reported normal CSF analysis had also been done there, which had been within normal limits The child was then admitted to our hospitalSeries of pediatric patients with GuillainBarre´ syndrome, evaluating the frequency of nerve root enhancement on spinal magnetic resonance imaging We sought to demonstrate that nerve root enhancement is a frequent finding in children with GuillainBarre´ syndrome, and that spinal magnetic resonance imaging should be performedSpine was negative for cervical hematoma and cord compression CPK to assess for myositis was normal Given the patient's clinical history of ascending paralysis with supporting physical exam findings, history of current COVID19 infection, and negative imaging, a working diagnosis of GuillainBarré Syndrome (GBS) was made



Role Of Mri Evaluation In Acute Secondary Inability To Walk In Children Egyptian Journal Of Radiology And Nuclear Medicine Full Text




Pdf Spinal Mri Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar
GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) is an acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy In typical cases, the first symptoms of GBS are pain, numbness, paresthesia, weakness in the limbs Autonomic involvement is common and causes urinary retention andIt has superficial similarities to a motor axonal variant of GuillainBarré syndrome but can be distinguished by clinical, cerebrospinal fluid, and, perhaps specifically, magnetic resonance imaging characteristics An MRI of the cervical spine showed an abnormal signal within the ventral gray matter of the spinal cordThe nerve conduction findings in GuillainBarre syndrome May be normal With pure demyelinationSlowed nerve conduction velocities, (temporal dispersion of waveforms, conduction block, prolonged or absent F waves) If axonopathyreduced amplitude The cerebral spinal fluid findings in Listeria meningitis



Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Covid 19 Disease Bmj Case Reports




Guillain Barre Syndrome Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
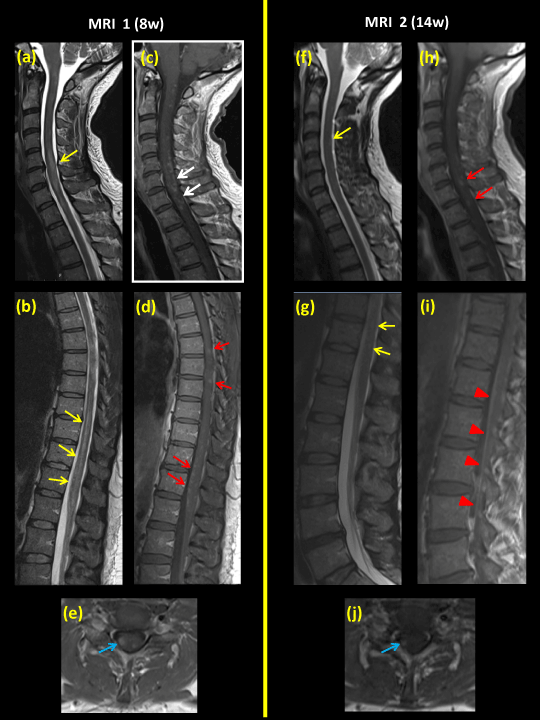
Spinal MRI with gadolinium frequently indicates enhancement of the spinal nerve roots early in the course of pediatric GBS, and aids clinicians in establishing a diagnosis early in the course of GuillainBarre syndrome after coronary artery bypass surgery Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 12;–9 Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar 2 Battaglia F, Sevy A, Moyse E, Roche PH GuillainBarré syndrome following severe head trauma and spine surgery Rev Neurol (Paris) 13;–8 Smith N, Pereira J, GrattanSmith P Investigation of suspected GuillainBarre syndrome in childhood What is the role for gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the spine?



Covid 19 Associated Bifacial Weakness With Paresthesia Subtype Of Guillain Barre Syndrome American Journal Of Neuroradiology



2
Study design A case report of Guillain–Barre Syndrome (GBS) variant presenting in a patient with high tetraplegia following cervical spinal cord lesion (C3C6) Objective To illustrate a clinical presentation of GBS in an individual with tetraplegia Miller Fisher syndrome (MFS) is characterized by the clinical triad of ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and areflexia (), whereas its site of lesions, particularly of ataxia, is a matter of controversy (2–5) As a variant form of GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS), MFS is generally thought to result from peripheral neuropathy (3, 6–8)Several MR imaging studies also have shown CNSAbstract and Figures GuillainBarré syndrome is a relatively common, acute, and rapidly progressive, inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy The diagnosis is



Cureus Synchronous Occurrence Of Guillain Barre Syndrome And Transverse Myelitis Of Unknown Etiology In An Adolescent



An Unusual Guillain Barre Syndrome Mimic A Case Of Spinal Adem And Review Of The Literature
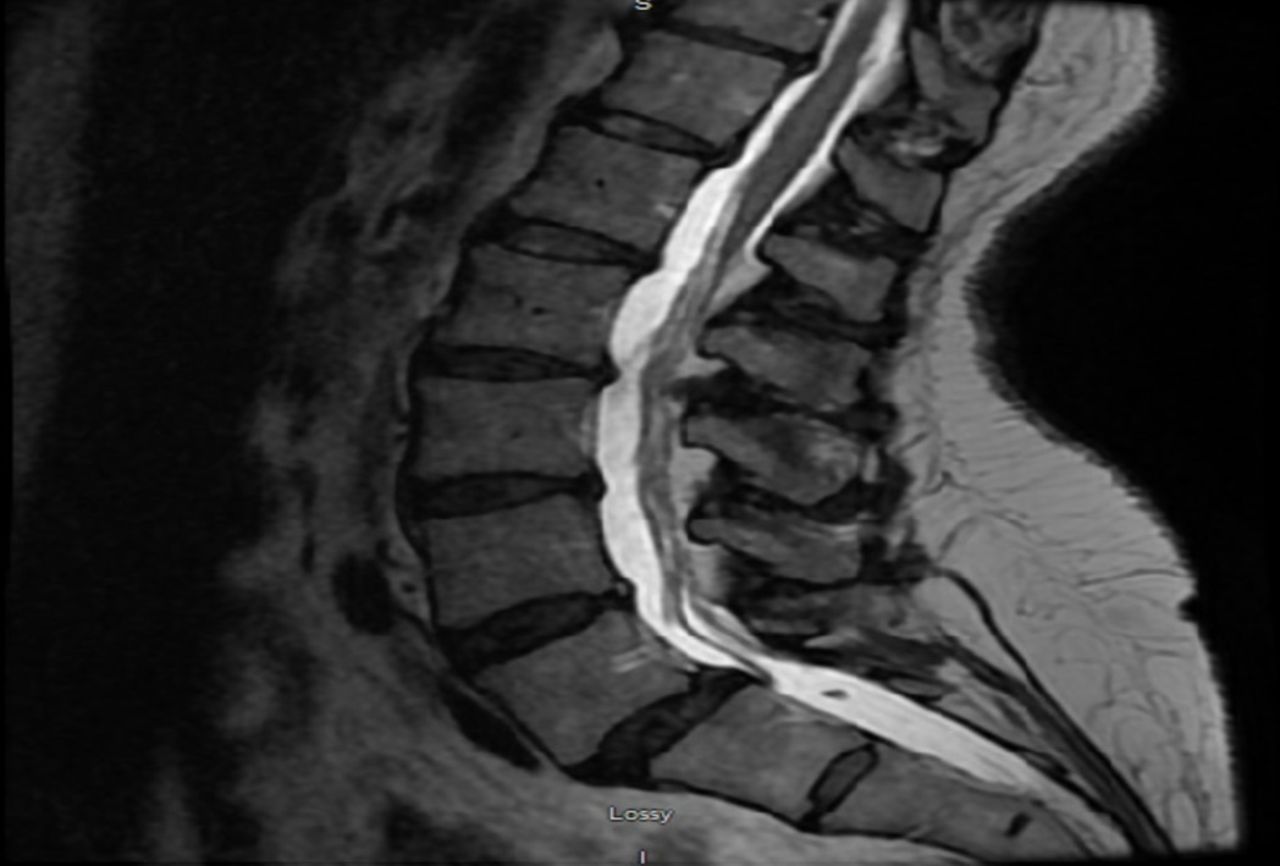
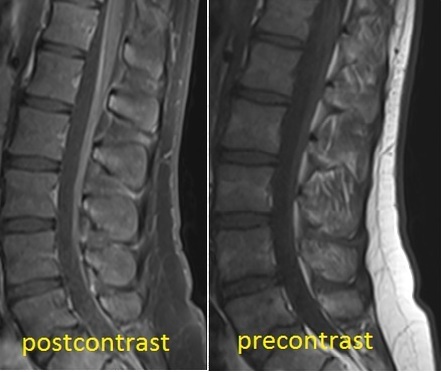
Introduction Patients with coronavirus disease 19 (COVID19) typically present with respiratory symptoms, but little is known about the disease's potential neurological complications We report a case of Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) following a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV2) infection, in association with leptomeningeal enhancement Keywords bilateral glossopharyngeal paralysis, pharyngealcervicalbrachial variant, guillainbarre syndrome (gbs) Introduction GuillainBarré Syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmunemediated peripheral neuropathy characterized by progressive symmetric motor weakness, sensory changes, hyporeflexia, and autonomic symptoms Clinical diagnosis Guillain Barre syndrome On admission MRI Sagittal T2 screening of whole spine for cord was normal MRI study of lumbar region repeated with intra venous contrast showed abnormal enhancement along nerve roots of cauda equina on post contrast T1w images consistent with clinical diagnosis of GB syndrome




Guillain Barre Syndrome Spine Mri Of A 64 Year Old Colombian Female Download Scientific Diagram
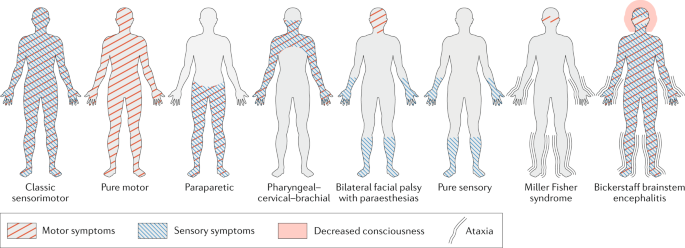



Diagnosis And Management Of Guillain Barre Syndrome In Ten Steps Nature Reviews Neurology
GuillainBarré syndrome is a rare occurrence in medicine and is probably rarer still as a postoperative complication We report an uneventful operative course, during epiduralgeneral anesthesia, in a patient undergoing pancreatectomy who presented with acute paralysis mimicking an acute cervical spinal cord syndrome or brachial plexus neuropathyMRI Although MRI is usually used to investigate patients with these symptoms, there can be no abnormalities 7 Multiple cranial nerves enhancement is reported, as it is with GuillainBarré syndrome 8 Treatment and prognosisFigure 1 MRI of the lumbar spine without contrast Learning points In the spectrum of neurologic manifestations of COVID19, GuillainBarré syndrome (GBS) should be considered in patients with peripheral nervous system symptoms Early recognition and treatment of GBS can prevent potentially serious morbidity and mortality in patients with
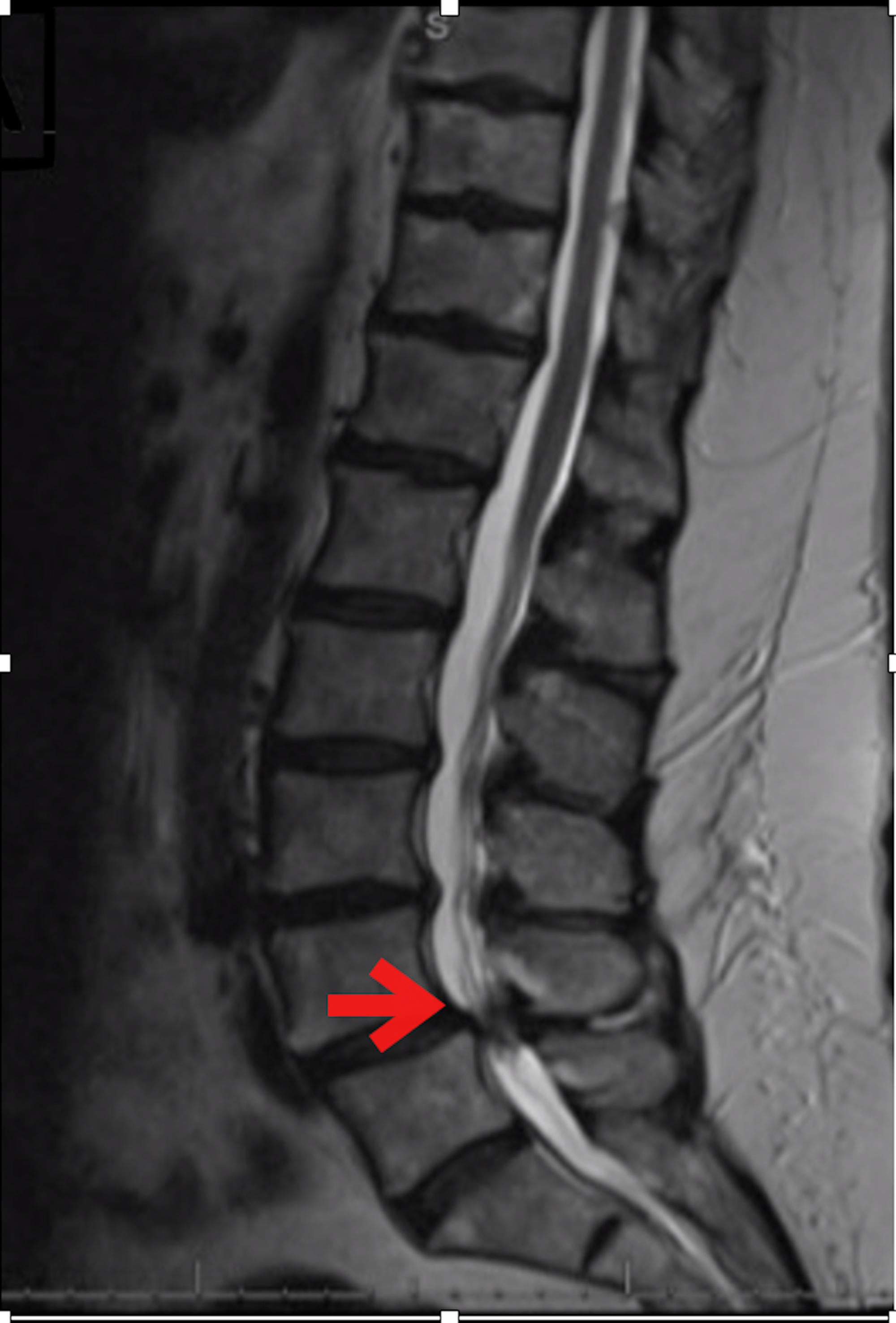



Cureus Guillain Barre Syndrome After Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion A Case Report




Clinical And Experimental Pediatrics
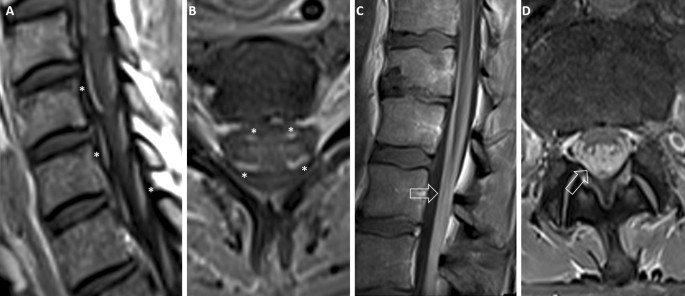
Guillain‐Barré syndrome is a rare disease primarily affecting the peripheral nervous system (PNS), often sparing the central nervous system (CNS) 1 It generally presents as an ascending areflexic motor weakness without incontinence while sparing sensation, 2 though there have been many variants described in literature which have varied presentations 3 The most GuillainBarré syndrome diagnosis is based on clinical presentation and supportive diagnostic testing In its early stage, no single, reliable diagnostic test is available However, a finding of nerve root enhancement on spinal magnetic resonance imaging may be useful We evaluated the frequency of nerve root enhancement on spinal magnetic resonance imaging in children with GuillainMR of the Spine in GuillainBarre Syndrome Bassem A Georgy, Brian Chong, Marc Chamberlain, John R Hesselink, and Gordon Cheung Summary MR examination of the spine after injection of gado pentetate dimeglumine showed enhancement of the cauda equina in a case of GuillainBarre syndrome These MR obser vations may help confirm the diagnosis of GuillainBarre syn drome




Pdf Spinal Mri Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar




Nerve Root Enhancement On Spinal Mri In Pediatric Guillain Barre Syndrome Pediatric Neurology
Age range, 247 years) with GuillainBarré syndrome were retrospectively reviewed GuillainBarré syndrome was diagnosed mainly on the basis ofRopper AH, Wijdicks EFM, Truax BT GuillainBarré syndrome, FA Davis, Philadelphia 1991 p57 Elahi A, Kelkar P, St Louis EK Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome as the initial manifestation of GuillainBarré SyndromeGuillain–Barré syndrome is a rapidonset muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation or pain often in the back along with muscle weakness, beginning in the feet and hands, often spreading to the arms and upper body The symptoms




Guillain Barre Syndrome The Lancet




Cureus Guillain Barre Syndrome After Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion A Case Report
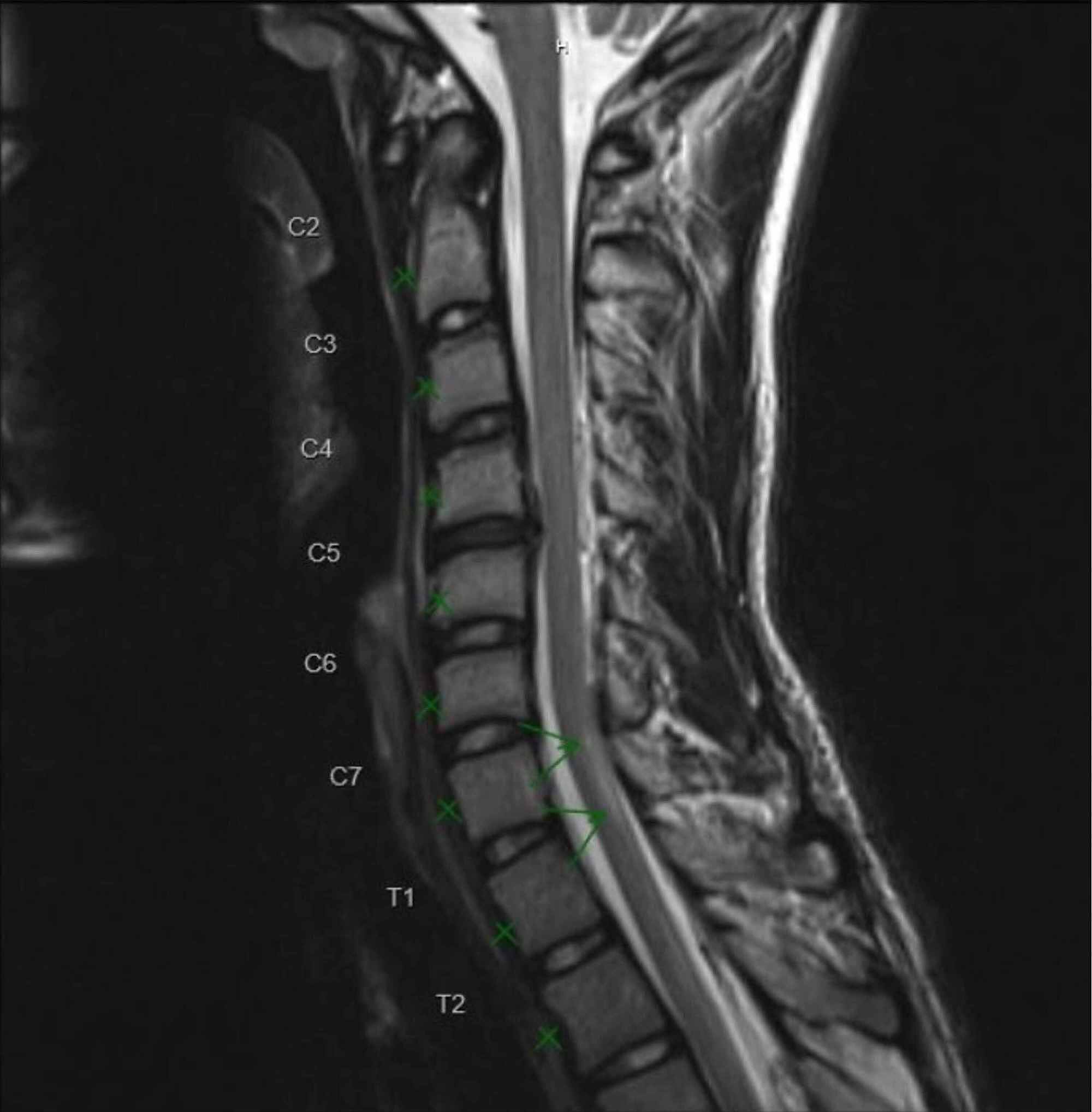
He was admitted with a presumptive diagnosis of GuillainBarre syndrome and was started on intravenous immunoglobulin Three days after admission, paresthesia ascended to the level of nipple line, and his weakness in the lower limb increased significantly MRI of the cervical spine showed focal nonenhancing lesions extending from C4 to C6GuillainBarre Syndrome (GBS) is an acute inflammatory polyradiculopathy It is immune mediated and causes ascending weakness in the limbs, respiratory failure and autonomic instability Synonyms LandryGuillainBarreStrohl syndrome Clinical features Progressive ascending weakness in both legs & arms & areflexia The 24 consecutive pediatric patients with GuillainBarré syndrome who underwent spinal magnetic resonance imaging included 11 girls and 13 boys, with a median age of 75 years ()Magnetic resonance imaging of the complete spine was performed in patients, and of the lumbosacral spine in 4 patients, with administration of gadolinium contrast ()




Atypical Guillain Barre Syndrome Misdiagnosed As Lumbar Spinal Stenosis




This Is Cervical Magnetic Resonance Image Which Was Taken With Symptoms Download Scientific Diagram
Pembrolizumab related Guillain barre syndrome, a rare presentation in a patient with a history of lupus and bladder cancer of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine which revealed multiple bony sclerotic lesions consistent with metastasis and multi focal lymphadenopathy contacted MRI of cervical thoracic and lumbar spineBrain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) abnormalities are present in only 30% of BBE cases and the frequency of BBE variant is 10% of that of MFS The pharyngealcervicalbrachial motor variant manifests in up to 3% with ptosis, facial, pharyngeal and neck flexor muscle weakness that spreads to the arms and spares leg strength, sensation and illness polyneuropathy and myopathy (CIP/CIM), or GuillainBarré Syndrome (GBS) and its variants An underlying disorder of the central nervous system (CNS), such as stroke, neuroinflammatory diseases, CNS infection, paraneoplastic syndrome or a spine lesion, is less likely but it should also be taken in account
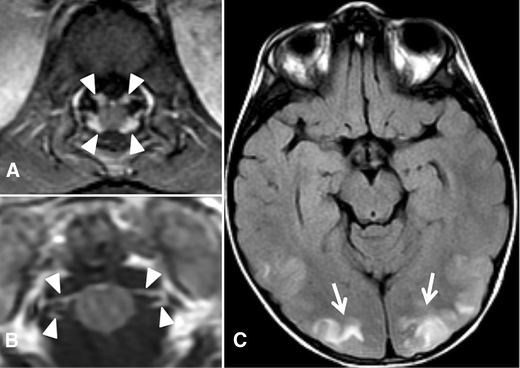



Guillain Barre Syndrome Related Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Springerlink




Pdf Spinal Mri Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome
The initial suggested diagnosis was Guillain‐Barré syndrome (GBS), though the neurophysiological examination turned out to be normal The various differential diagnosis challenge of this case began after the unexpected spinal MRI results Case report Saifudheen K, Jose J, Gafoor VA, Musthafa M GuillainBarre syndrome and SIADH Neurology 11;




Mri Of The Cervical Nerve Roots In The Diagnosis Of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy A Single Institution Retrospective Case Control Study Bmj Open




Pdf Spinal Mri Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar
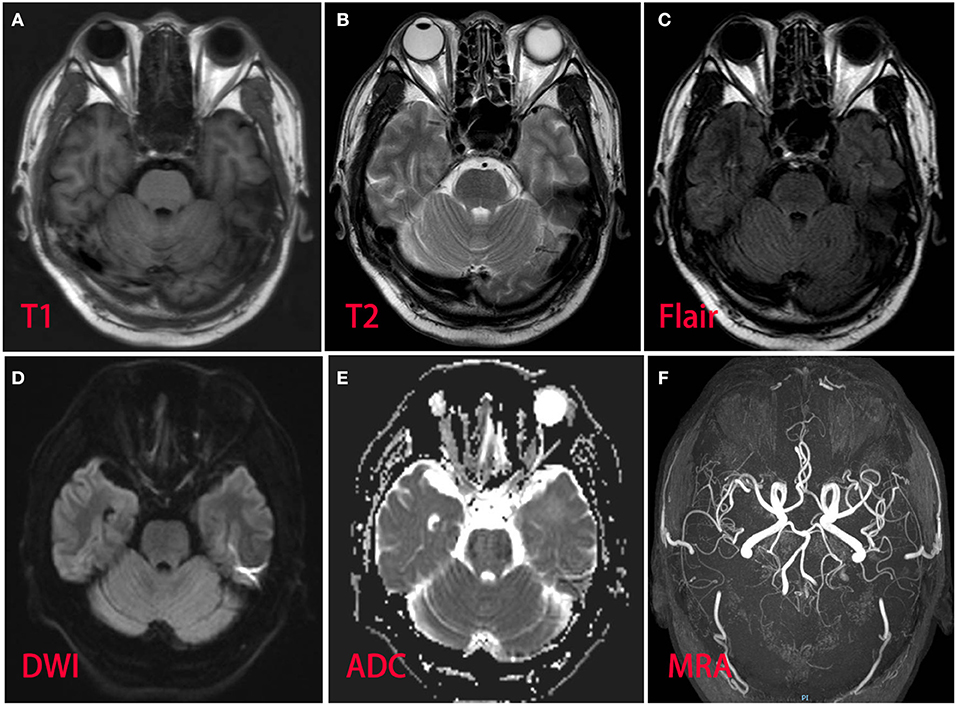



Frontiers Case Report Early Onset Guillain Barre Syndrome Mimicking Stroke Neurology




Nerve Root Enhancement On Spinal Mri In Pediatric Guillain Barre Syndrome Pediatric Neurology
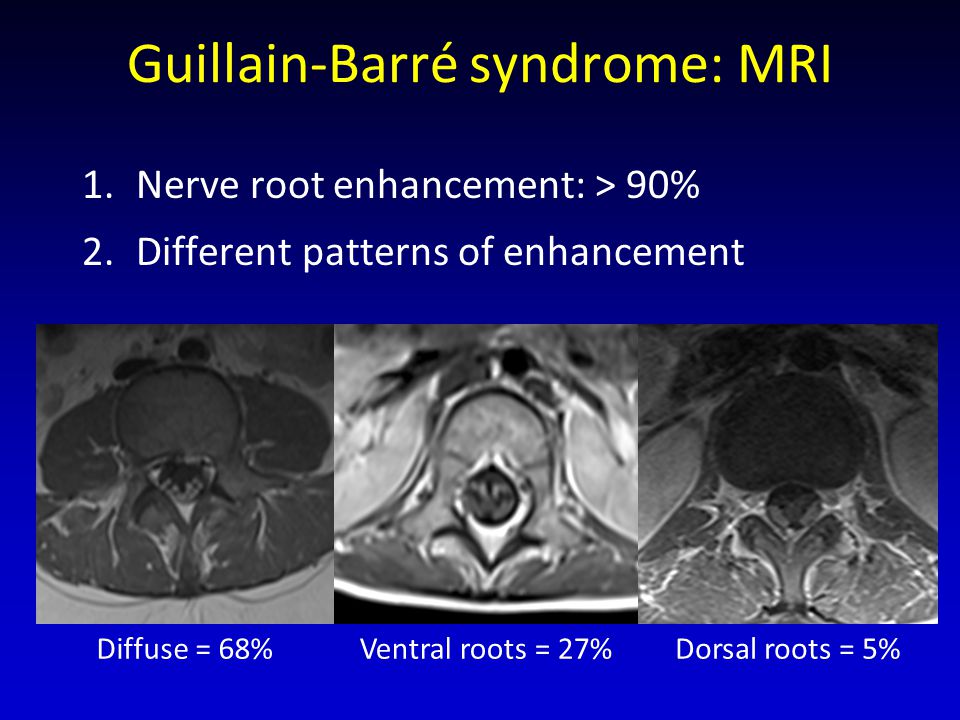



Eede Pediatric Spinal Nerve Root Enhancement Clinical And Differential Considerations Marinos Kontzialis1 Hans Michell2 Andrea Poretti2 Thierry Ppt Download




Enhancement Of Cranial Nerves Conus Medullaris And Nerve Roots In Polg Mitochondrial Disease Neurology Genetics
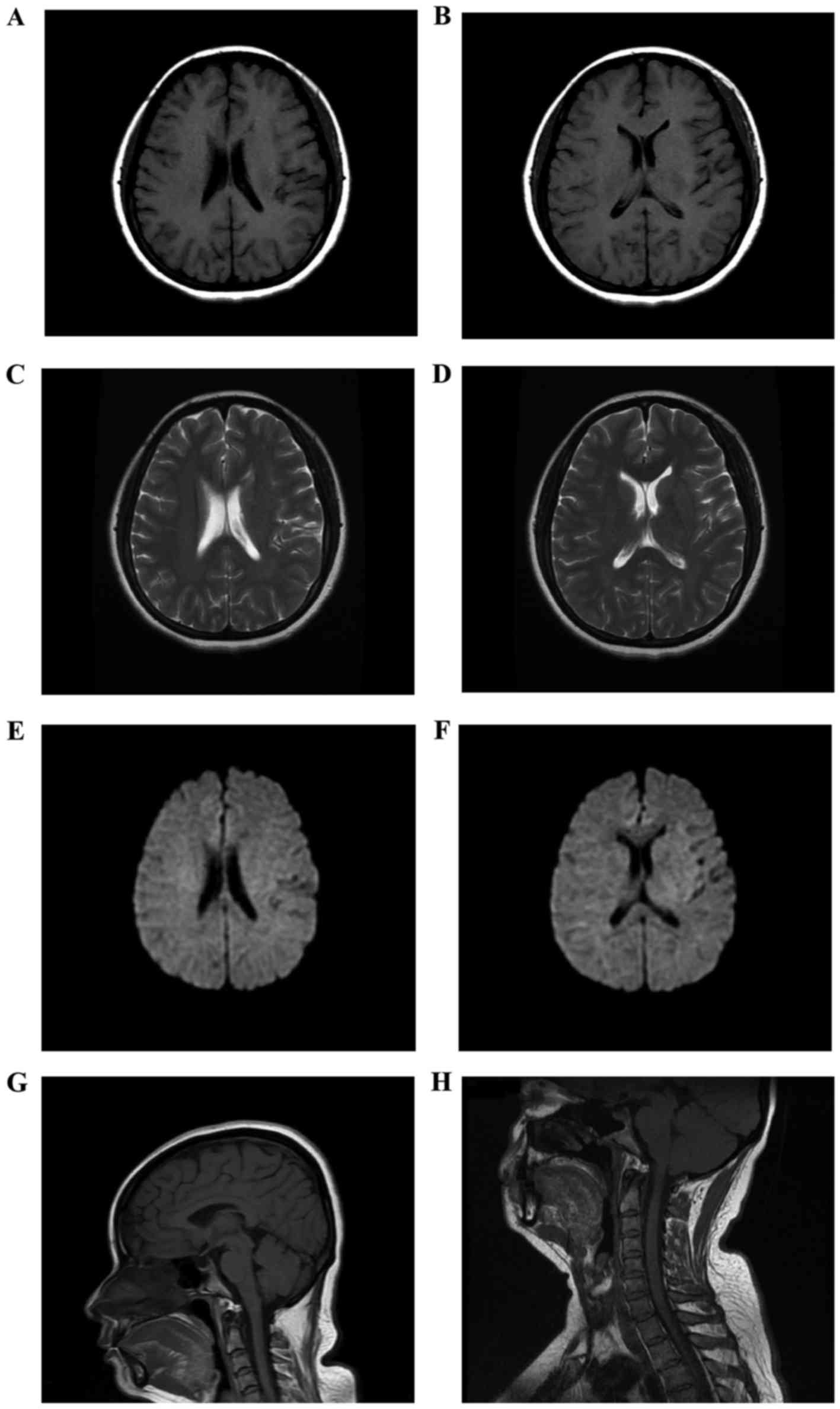



Acute Bilateral Vision Deficit As The Initial Symptom In Guillain Barre Syndrome A Case Report



Mr Imaging Findings Of Spinal Posterior Column Involvement In A Case Of Miller Fisher Syndrome American Journal Of Neuroradiology




Young Woman With Guillain Barre Syndrome And Cervical Transverse Myelitis A New Gbs Variant Not Coincidence Gharzeddine Clinical Case Reports Wiley Online Library




Pdf Spinal Mri Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar
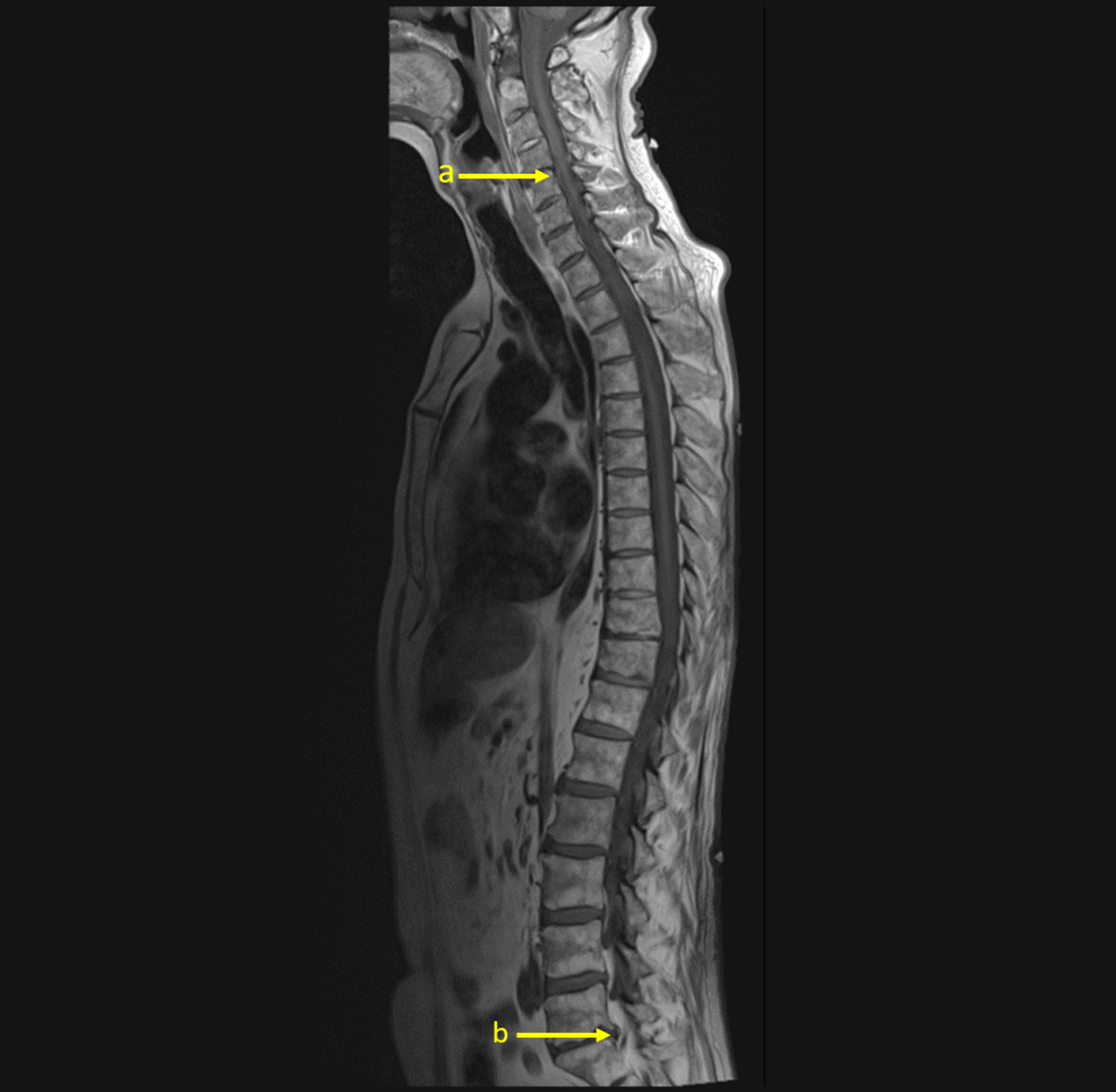



Cureus A Case Of Paraneoplastic Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Lung
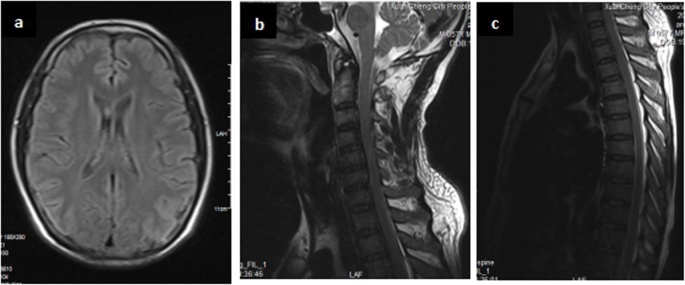



Severe Guillain Barre Syndrome After Surgery For Multiple Fractures A Rare Case Report With A 5 Year Follow Up And A Brief Review Of The Literature Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders Full Text




Scielo Brasil Guillain Barre Syndrome As A Differential Diagnosis Of Low Back Pain Syndrome Guillain Barre Syndrome As A Differential Diagnosis Of Low Back Pain Syndrome




Miller Fisher Syndrome With Cognitive Im Biomedical Research




Nerve Root Enhancement On Spinal Mri In Pediatric Guillain Barre Syndrome Pediatric Neurology




An Unusual Descending Presentation Of Pediatric Guillain Barre Syndrome Following Covid 19 Expanding The Spectrum Pediatric Neurology




A Rare Case With New Insights Pure Sensory Guillain Barre Syndrome Wi Imcrj




Sulcal Abnormalities On Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging In The Guillain Barre Syndrome Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry




Guillain Barre Syndrome In A Child With Covid 19 Infection American Academy Of Pediatrics




Post Traumatic And Postsurgical Guillain Barre Syndrome A Rare But Treatable Entity Bmj Case Reports



Pure Sensory Guillain Barre Syndrome A Case Report And Review Of The Literature



Neurology International Free Full Text A Novel Case Of Bifacial Diplegia Variant Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Following Janssen Covid 19 Vaccination Html



Covid 19 Associated Bifacial Weakness With Paresthesia Subtype Of Guillain Barre Syndrome American Journal Of Neuroradiology




Medpix Case Guillain Barre Syndrome



Guillain Barre Syndrome Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org




Pdf Spinal Mri Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar




Guillain Barre Syndrome Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Acute Polyradiculoneuritis With Locked In Syndrome In A Patient With Covid 19 Springerlink
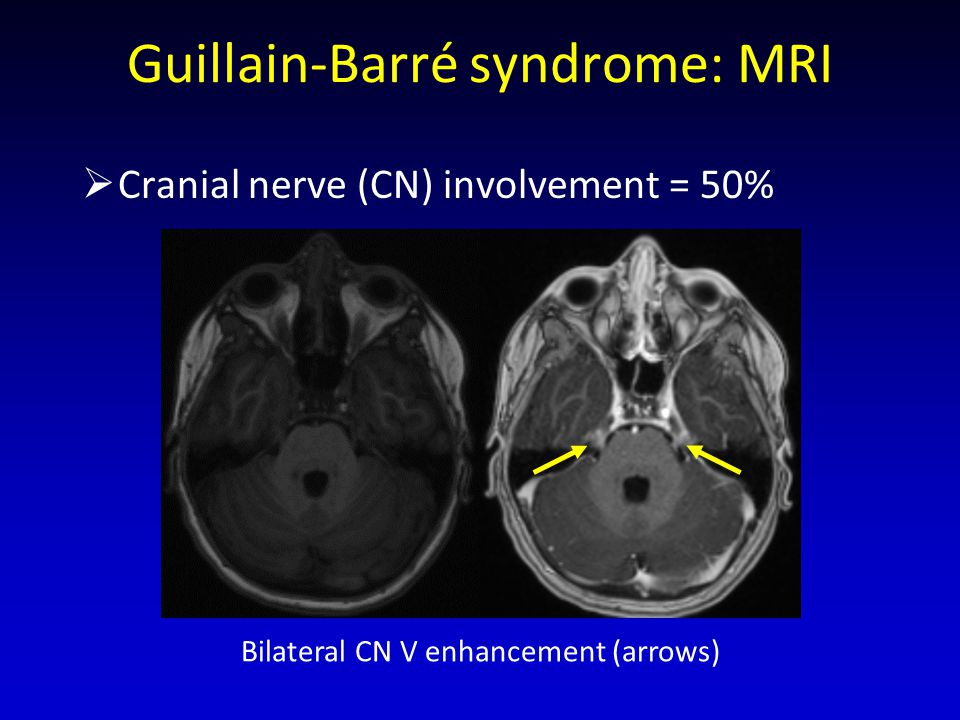



Eede Pediatric Spinal Nerve Root Enhancement Clinical And Differential Considerations Marinos Kontzialis1 Hans Michell2 Andrea Poretti2 Thierry Ppt Download




Guillain Barre Syndrome Spine Mri Of A 42 Year Old Colombian Male With Download Scientific Diagram
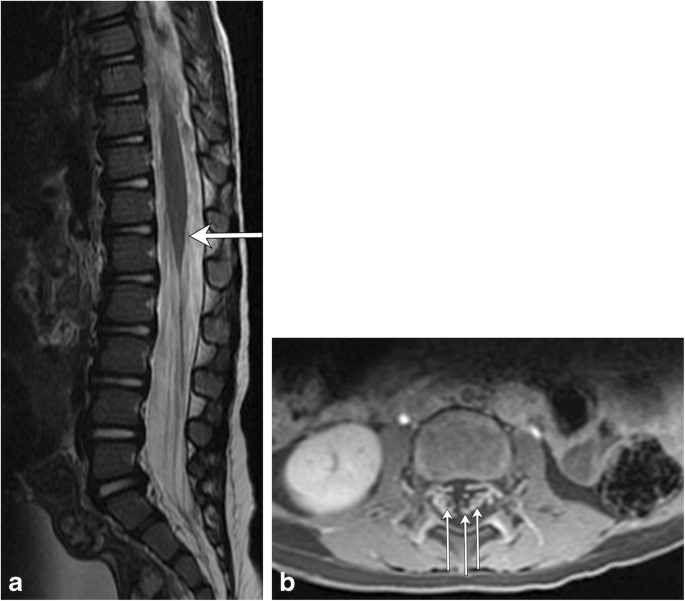



Location Length And Enhancement Systematic Approach To Differentiating Intramedullary Spinal Cord Lesions Insights Into Imaging Full Text




Scielo Brasil Guillain Barre Syndrome As A Differential Diagnosis Of Low Back Pain Syndrome Guillain Barre Syndrome As A Differential Diagnosis Of Low Back Pain Syndrome




Concurrent Guillain Barre Syndrome Transverse Myelitis And Encephalitis Post Zika A Case Report And Review Of The Pathogenic Role Of Multiple Arboviral Immunity Sciencedirect




Cervical Spine Surgery Complicated By Postoperative Guillain Barre Syndrome Sciencedirect



1
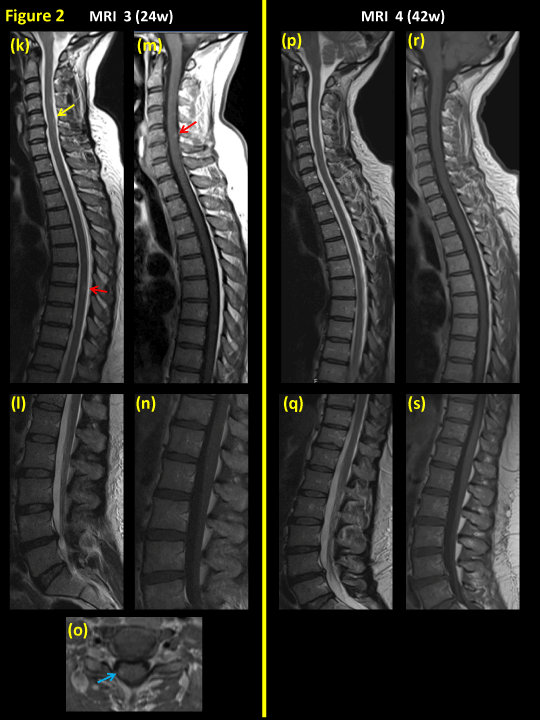



An Unusual Guillain Barre Syndrome Mimic A Case Of Spinal Adem And Review Of The Literature




Guillain Barre Syndrome Presenting With An Angina Mimic And Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Rcp Journals




Figure 1 An Unusual Case Of Recurrent Guillain Barre Syndrome Of A Different Subtype Five Years After Initial Diagnosis



Neuroimaging Findings Of Zika Virus Associated Neurologic Complications In Adults American Journal Of Neuroradiology
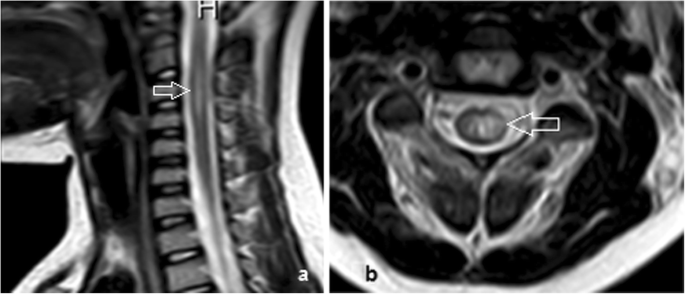



Role Of Mri Evaluation In Acute Secondary Inability To Walk In Children Egyptian Journal Of Radiology And Nuclear Medicine Full Text
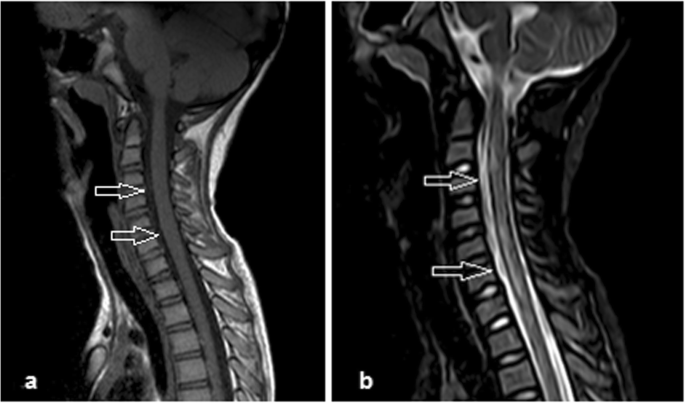



Role Of Mri Evaluation In Acute Secondary Inability To Walk In Children Egyptian Journal Of Radiology And Nuclear Medicine Full Text
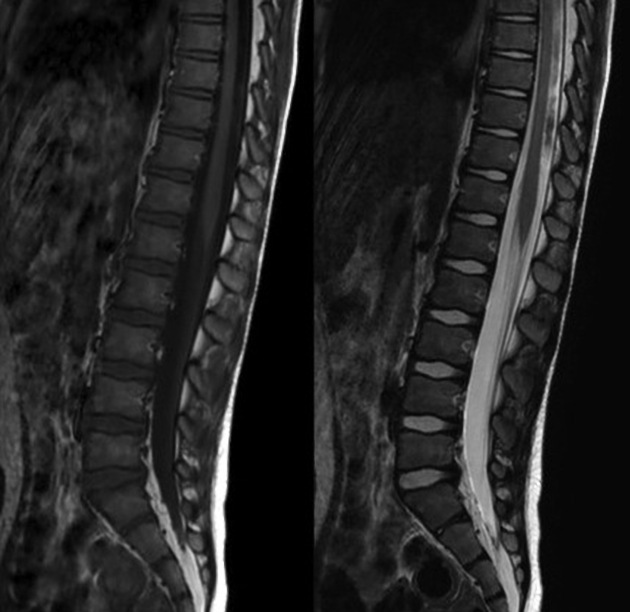



Guillain Barre Syndrome Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org




Cerebral White Matter Lesions In Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy Neurology




Mri Of The Spinal Cord In A 3 Year Old Boy With Guillain Barre Download Scientific Diagram




Spinal Nerve Pathology In Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Covid 19 Infection Berciano Muscle Amp Nerve Wiley Online Library
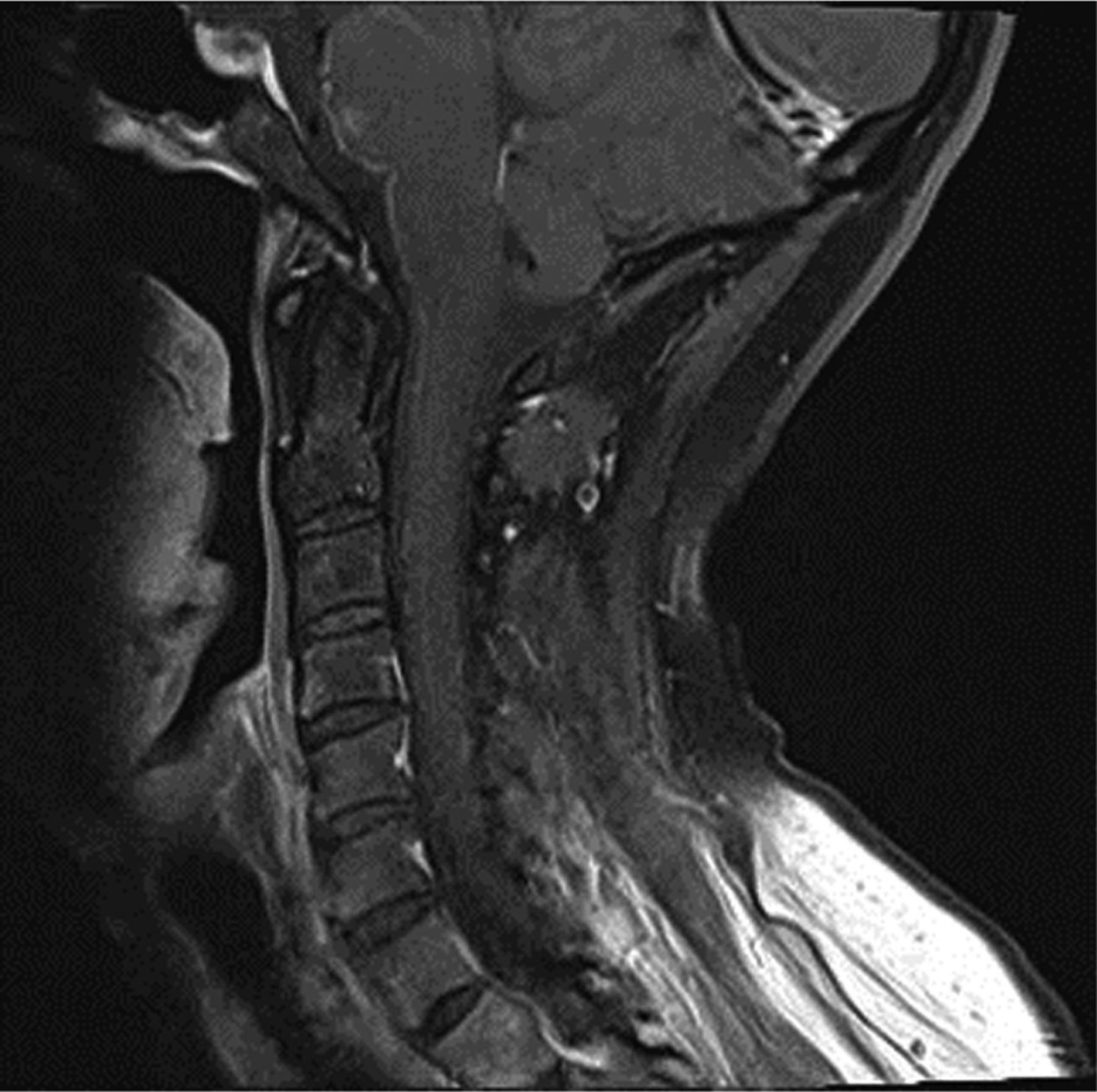



Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Leptomeningeal Enhancement Following Sars Cov 2 Infection Rcp Journals
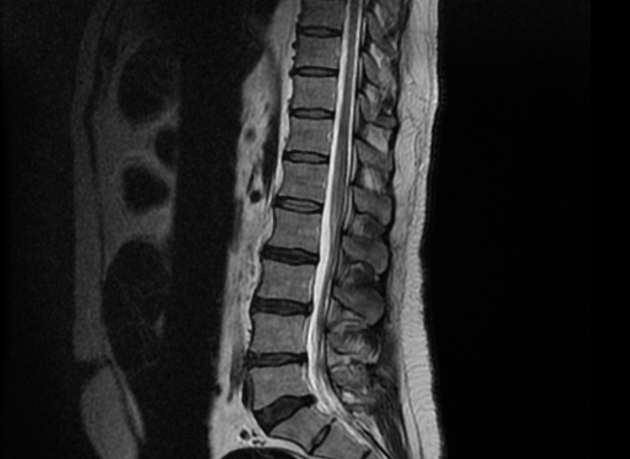



Guillain Barre Syndrome Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
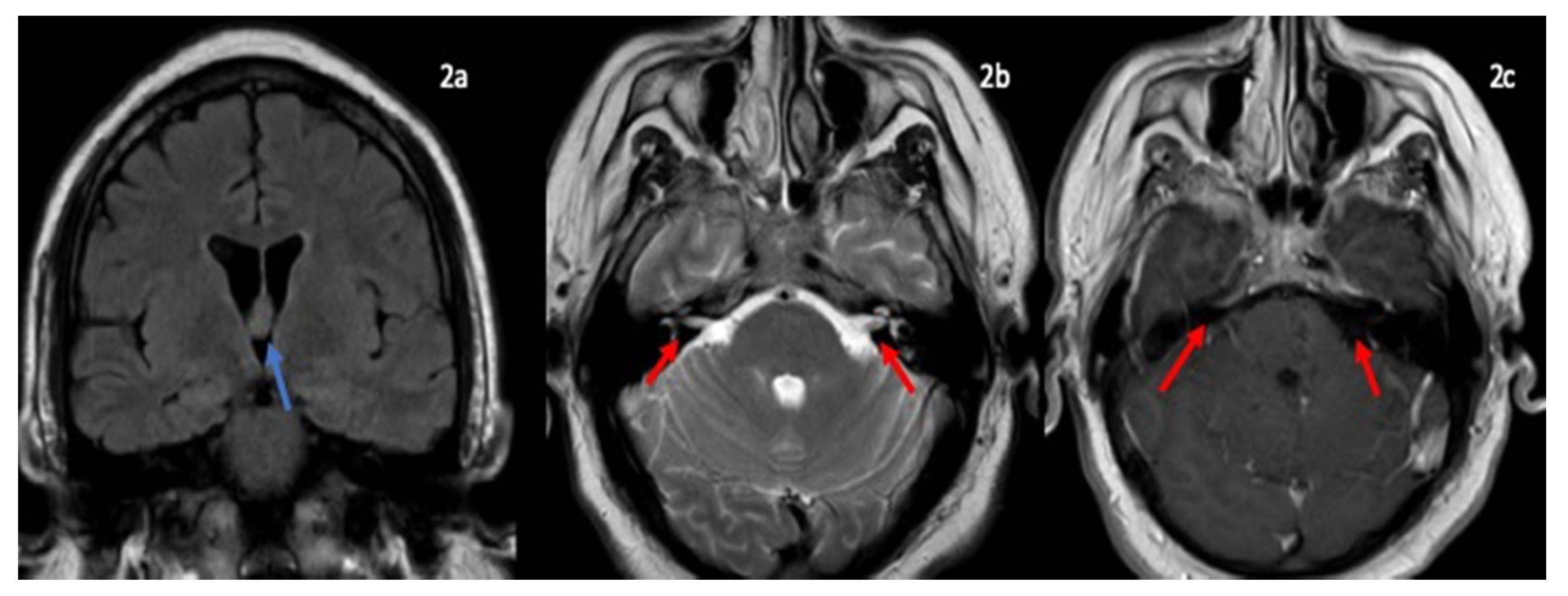



Neurology International Free Full Text A Novel Case Of Bifacial Diplegia Variant Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Following Janssen Covid 19 Vaccination Html



1




Unilateral Facial Palsyin Guillain Barre Syndrome A Hyperreflexic Variant Case European Medical Journal




Dr Balaji Anvekar Frcr Guillain Barre Syndrome Mri




Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Covid 19 Infection A Case Report Journal Of Clinical Neuroscience
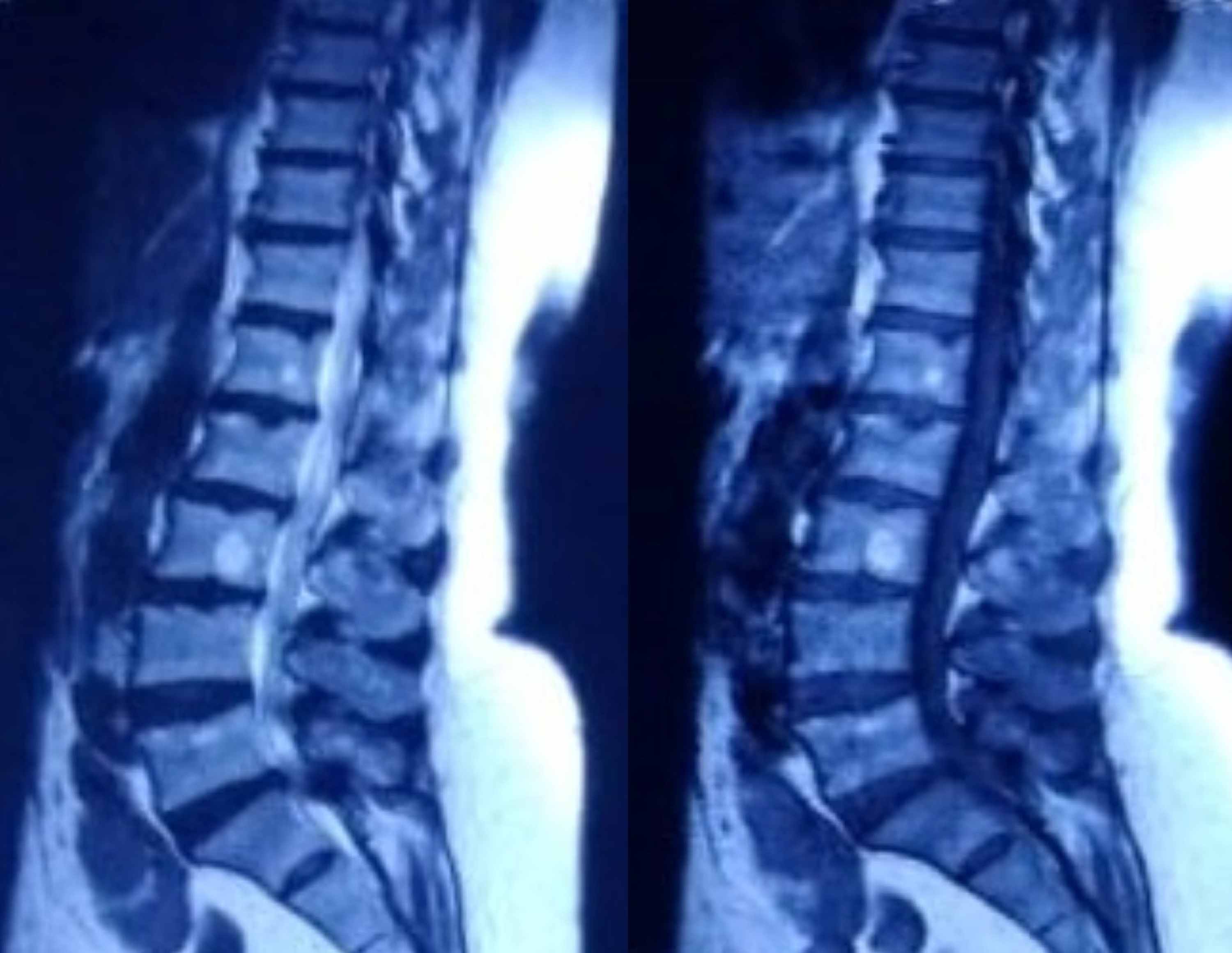



Cureus Association Of Guillain Barre Syndrome With Covid 19 A Case Report And Literature Review



Guillain Barre Syndrome Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
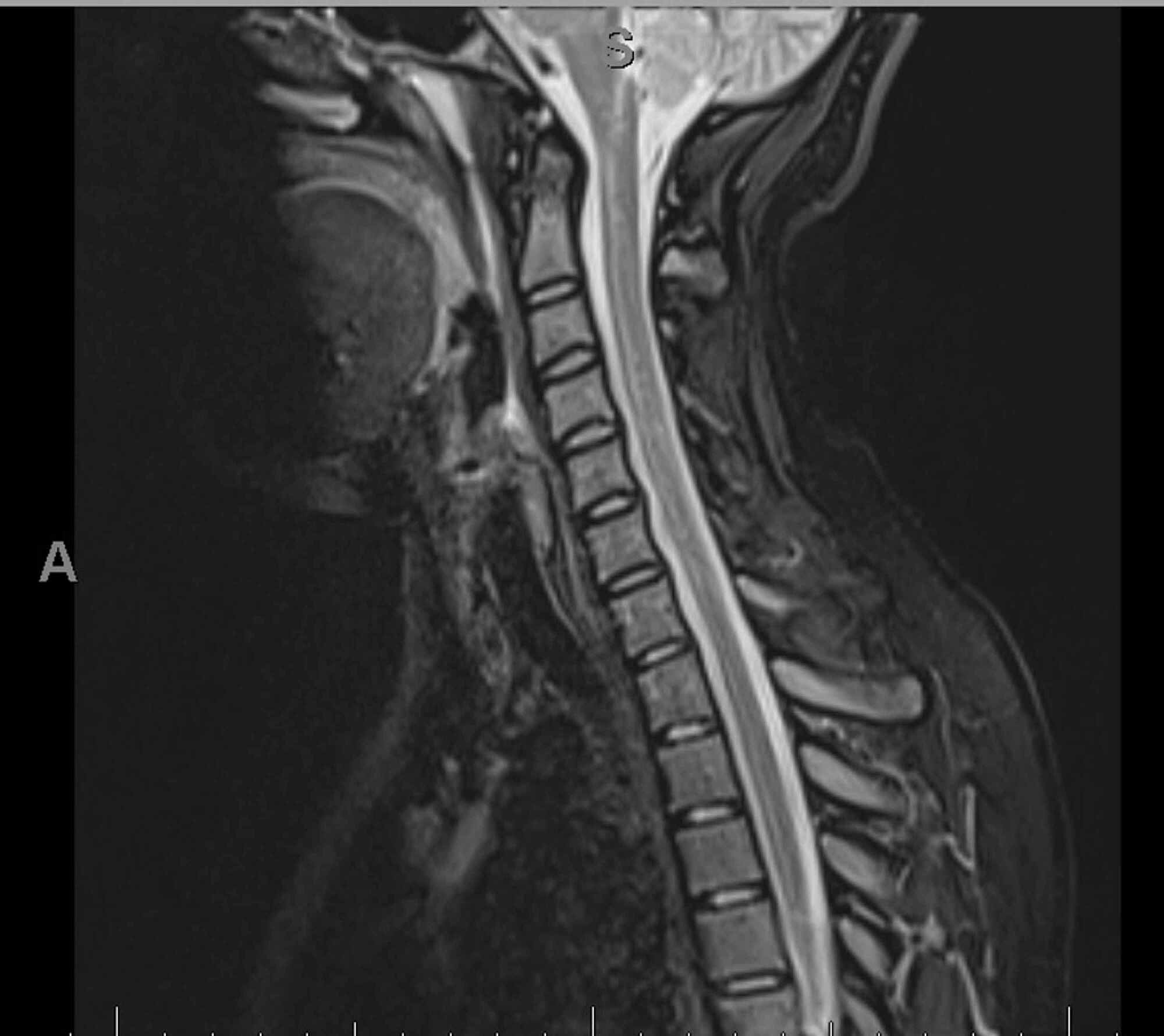



Cureus Guillain Barre Syndrome Associated With Covid 19 Infection A Case Report With Review Of Literature



Guillain Barre Syndrome
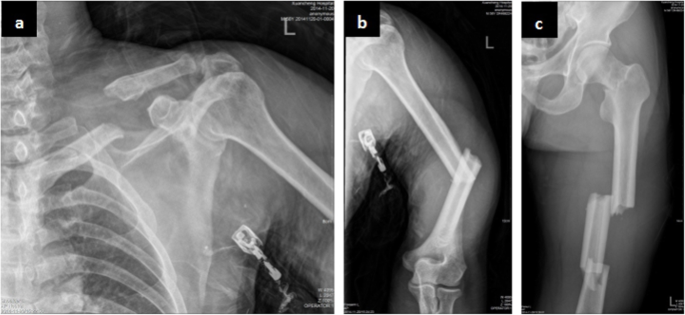



Severe Guillain Barre Syndrome After Surgery For Multiple Fractures A Rare Case Report With A 5 Year Follow Up And A Brief Review Of The Literature Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders Full Text



2




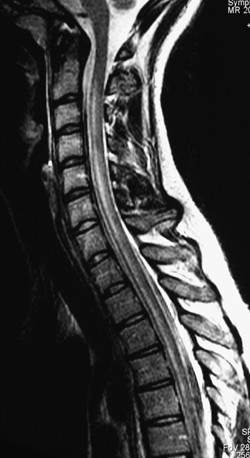
Teaching Neuroimages Variant Of Guillain Barre Syndrome With Spinal Cord Involvement Neurology




Concurrent Guillain Barre Syndrome Transverse Myelitis And Encephalitis Post Zika A Case Report And Review Of The Pathogenic Role Of Multiple Arboviral Immunity Sciencedirect



Cauda Equina Mri Findings Shefalitayal



Guillain Barre Syndrome Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org



1



Covid 19 Associated Bifacial Weakness With Paresthesia Subtype Of Guillain Barre Syndrome American Journal Of Neuroradiology




Guillain Barre Syndrome Spine Mri Of A 38 Year Old Iranian Female With Download Scientific Diagram




Guillain Barre Syndrome And Its Variants As A Manifestation Of Covid 19 A Systematic Review Of Case Reports And Case Series Journal Of The Neurological Sciences




Young Woman With Guillain Barre Syndrome And Cervical Transverse Myelitis A New Gbs Variant Not Coincidence Gharzeddine Clinical Case Reports Wiley Online Library




Pdf Spinal Mri Findings Of Guillain Barre Syndrome Semantic Scholar




Guillain Barre On Mri Stock Image C027 1712 Science Photo Library



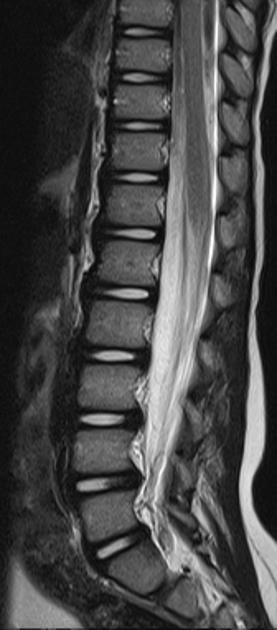
Cureus Guillain Barre Syndrome After Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion A Case Report



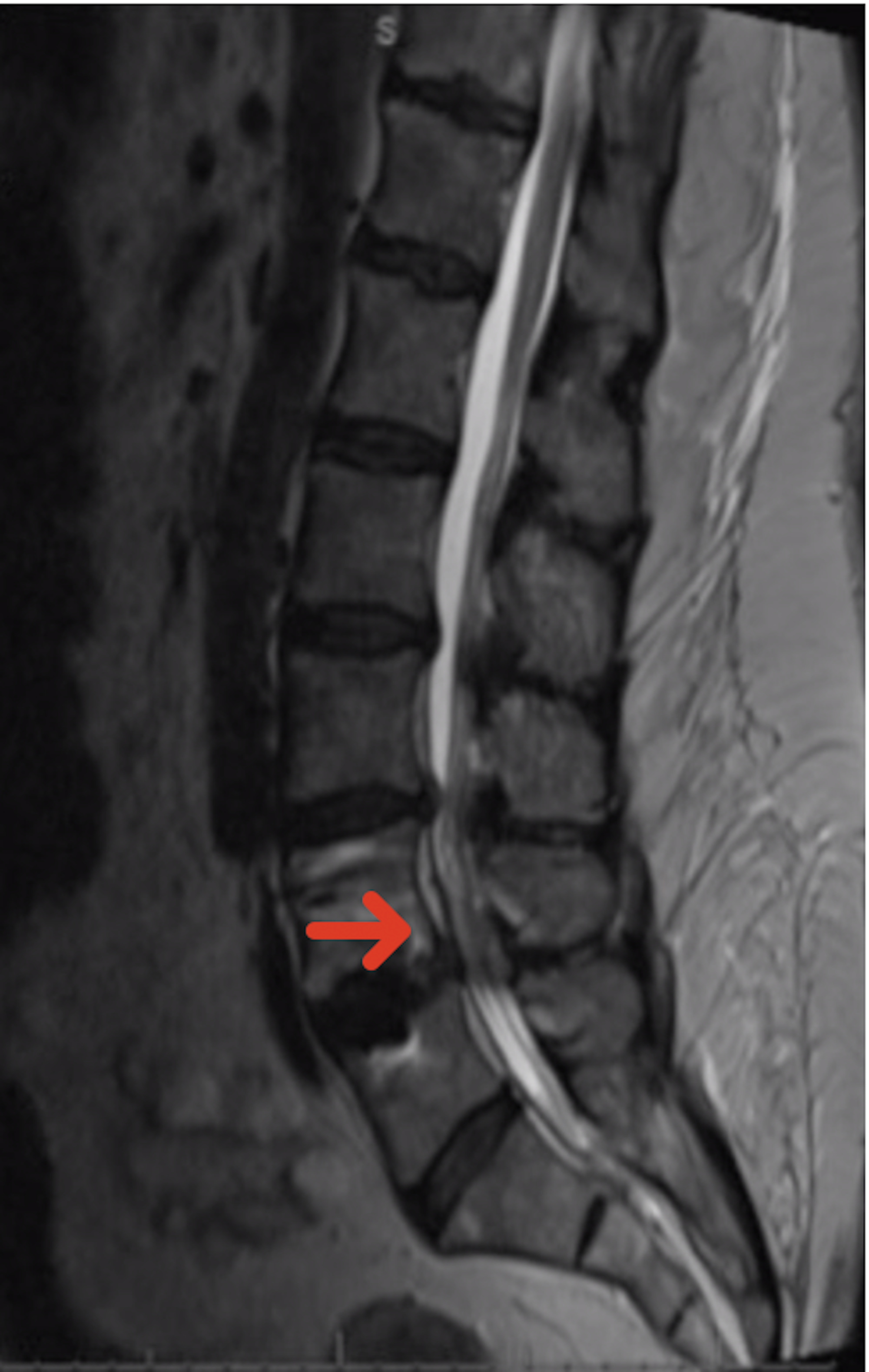
Campylobacter Jejuni Induced Acute Transverse Myelitis Spinal Cord
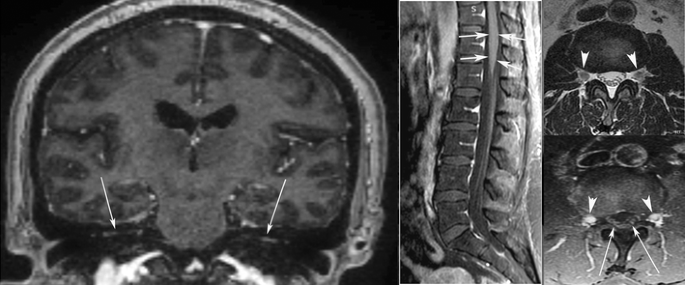



Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings In Guillain Barre Syndrome Caused By Zika Virus Infection Springerlink
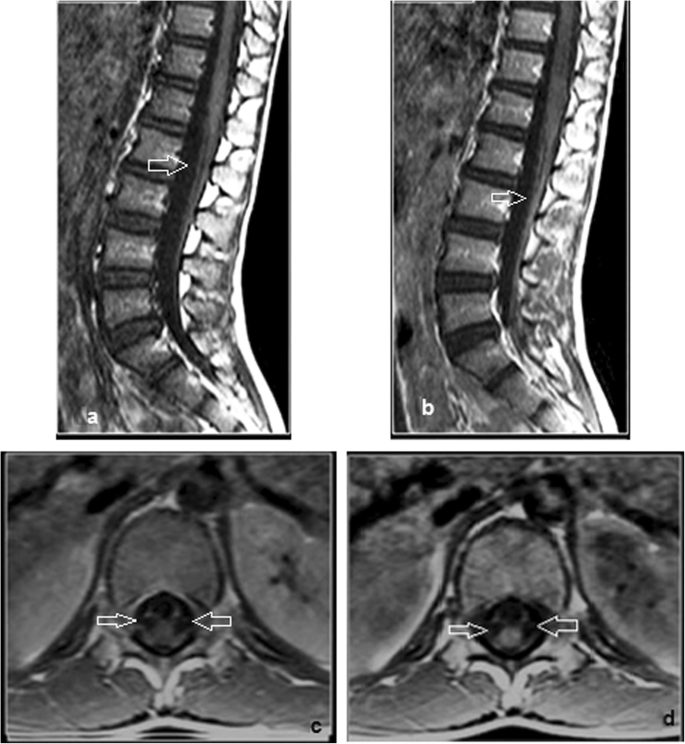



Role Of Mri Evaluation In Acute Secondary Inability To Walk In Children Egyptian Journal Of Radiology And Nuclear Medicine Full Text



2



Mr Imaging Findings Of Spinal Posterior Column Involvement In A Case Of Miller Fisher Syndrome American Journal Of Neuroradiology




Figure 1 An Unusual Case Of Recurrent Guillain Barre Syndrome Of A Different Subtype Five Years After Initial Diagnosis
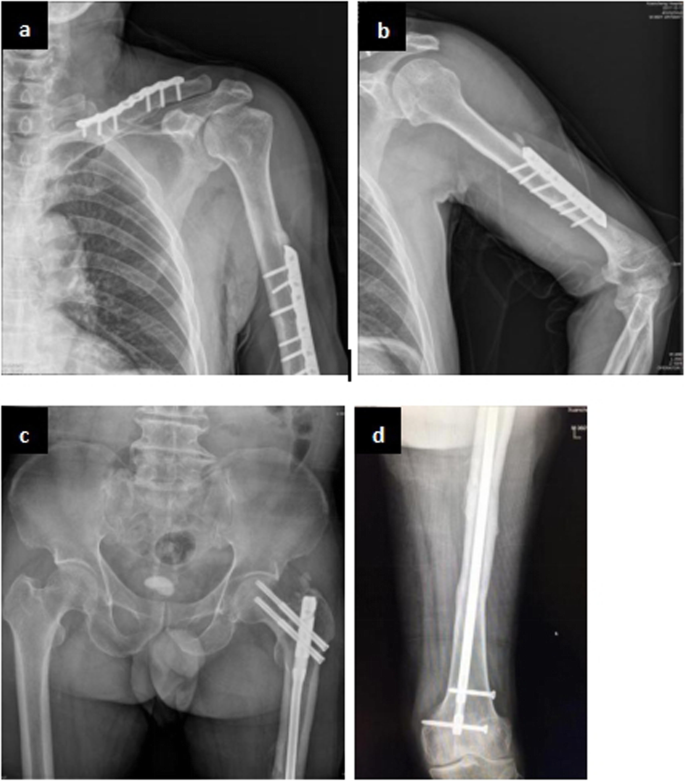



Severe Guillain Barre Syndrome After Surgery For Multiple Fractures A Rare Case Report With A 5 Year Follow Up And A Brief Review Of The Literature Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders Full Text
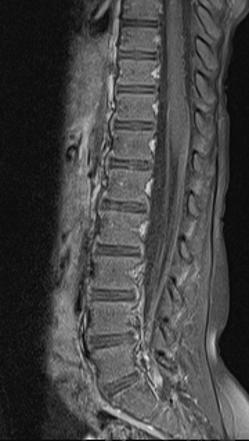



Guillain Barre Syndrome Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org




Incomplete Cord Syndromes Clinical And Imaging Review Radiographics




Case 3 Pain And Weakness In A 12 Year Old Boy American Academy Of Pediatrics




Incomplete Cord Syndromes Clinical And Imaging Review Radiographics




Nerve Root Enhancement In Guillain Barre Syndrome Practical Neurology



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿